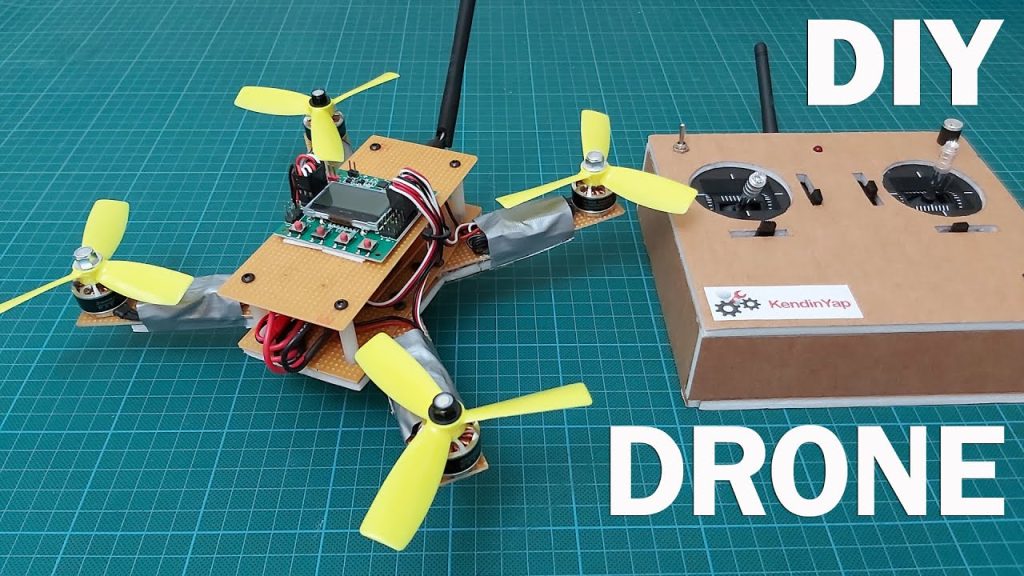
To make a drone at home, start by gathering all necessary components such as motors, propellers, a frame, and a controller. Assemble these parts according to your chosen design scheme, ensuring a balanced structure.
Building a drone at home has become a popular project for enthusiasts and hobbyists alike. With the right tools and basic understanding of electronics and aerodynamics, anyone can construct a custom drone. This DIY approach allows for customization and a deeper appreciation of the complexities involved in drone technology.
The core elements include a frame to hold everything together, motors to provide lift, propellers to generate thrust, and a flight controller to manage stability and direction. A remote control system is also essential for piloting your homemade aerial device. By carefully selecting and assembling these parts, you can create your very own drone tailored to your specifications and intended use, from photography to racing or just recreational flying.
Introduction To Diy Drones
The dream of flying doesn’t just belong to the skies anymore. Building a drone from scratch has become a reality that many enthusiasts and hobbyists are embracing. With today’s technology, anyone can create a custom drone at home. This introduction navigates through the basics of DIY drones, offering insight into their growing popularity and potential applications.
Growing Popularity
Drones are no longer exclusive to professionals. DIY drone projects have soared in popularity. They combine technology, creativity, and learning in an exciting way. People of all ages can now experience the thrill of crafting their own flying machines.
- Affordable components
- Accessible tutorials
- Supportive communities
Potential Applications
Homemade drones are not just for fun. They serve multiple practical purposes. The applications range from education and research to agriculture and photography. Below is a list of potential uses for your DIY drone:
- Aerial photography and videography
- Wildlife monitoring
- Precision agriculture
- Search and rescue operations
- Educational projects

Credit: www.instructables.com
Understanding Drone Basics
Drones are thrilling both hobbyists and professionals alike. Building a drone at home is not just an exciting project, but also a great way to understand the science behind these flying machines. Before getting your hands on the tools and parts, let’s dive into the fundamental knowledge required to create your very own flying marvel.
Types Of Drones
Drones come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for different purposes. Knowing the types helps you decide which one to build:
- Multirotor Drones: Easiest to make and control. They are perfect for beginners.
- Fixed-Wing Drones: Look like airplanes. They fly faster and longer but are harder to build.
- Single-Rotor Drones: Look like mini helicopters. They are more complex but efficient.
Essential Components
Every drone requires some key parts to fly. These are the essentials:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | The skeleton that holds all parts together. |
| Motors | They spin the propellers to lift the drone. |
| ESC (Electronic Speed Controller) | Controls the motor speed. |
| Propellers | Push air to create lift. |
| Battery | Powers the whole drone. |
| Flight Controller | The brain of the drone that manages its movement. |
| Receiver and Transmitter | Communication devices to control the drone remotely. |
Armed with this basic knowledge, you are one step closer to making your own drone. Ensure you select the right type of drone and gather all the essential components. Building a drone can be a fun learning experience, so start planning, and you’ll soon watch your home-built drone soar into the sky!
Planning Your Drone Build
Embarking on your very own drone build is an exhilarating project. Creating a drone from scratch requires foresight and careful planning. Whether for leisure, photography, or engineering, your journey begins here with a well-thought-out plan. Understanding the hurdles ahead ensures a smoother flight path to success.
Setting Objectives
Setting clear goals for your drone is essential. Ask yourself, what do you want your drone to do? Your objectives could include aerial photography, racing, or simple backyard flying. Knowing your end goal shapes all other decisions, from design to the components you’ll choose.
- Define the purpose: photography, racing, or recreation.
- Choose a design: fixed-wing or multi-rotor.
- Performance needs: speed, stability, and battery life.
Budgeting & Costs
A realistic budget is critical. Different requirements lead to different expenses. Building a drone can range from affordable to a significant investment. Itemize each component and check prices from multiple sources.
| Item | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Frame | $20 – $100 |
| Motors (x4) | $40 – $200 |
| Electronic Speed Controls (x4) | $20 – $100 |
| Flight Controller | $20 – $250 |
| Battery | $10 – $50 |
| Propellers (x4) | $5 – $20 |
| Radio Transmitter & Receiver | $30 – $200 |
Check for kit options that provide everything you need. Always count in extra for tools and spare parts. Keep in mind shipping costs and possible tax on the items.
Tools And Equipment Needed
Embarking on the journey of building a drone at home is an exhilarating venture. It requires precision, passion, and the right set of tools. The following sections detail essential tools and equipment to transform your drone project from a pile of components into a soaring reality.
Soldering Essentials
Soldering is pivotal in assembling a drone. Achieve strong electrical connections with the proper soldering equipment.
- Soldering Iron: A tool to heat the solder and apply it to connections.
- Solder: Metal alloy for creating bonds between components.
- Soldering Stand: Keeps the iron safe when not in use.
- Soldering Tip Cleaner: Cleans the iron’s tip for better performance.
- Safety Glasses: Protects eyes from any soldering splatter.
Software And Programming Tools
Software tools bring your drone to life. They allow you to program and control the drone’s behavior.
- Integrated Development Environment (IDE): A software suite for code editing and compiling.
- Drone Firmware: The foundational software required for drone operation.
- Flight Control Software: Enables tuning and customization of flight characteristics.
- USB Cable: Connects the drone’s flight controller to your computer.
- Proprietary Software: Some drones require brand-specific software for programming.
Ensure to have a clean workspace, with every tool within easy reach, to facilitate a seamless building experience.
Selecting The Frame
Building a drone starts with the right frame. Think of it as the skeleton of your homemade flying buddy. The frame holds all the parts together. A sturdy and well-designed frame is a must for a stable flight. Let’s guide you through choosing the perfect frame for your DIY drone project.
Material Considerations
The frame’s material affects durability and performance. Different materials offer unique benefits:
- Carbon Fiber: It’s light and super strong, ideal for racing drones.
- Aluminum: A great choice for strength, but slightly heavier.
- Plastic: Easy to find and cheap, perfect for beginner builds.
- Wood: Surprisingly strong and easy to work with at home.
Size And Weight
Size and weight are crucial for flight time and manoeuvrability. Bigger isn’t always better. The right balance is key.
| Size (in inches) | Weight | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Under 7″ | Light | Indoor fun and practice |
| 7″ to 12″ | Medium | Outdoor and racing |
| Over 12″ | Heavier | Advanced flying and filming |
Pick a frame that balances weight with the intended use for your drone. Ensure it fits the motors and rotors you plan to use. A well-chosen frame lays the foundation for an amazing drone experience.
Choosing The Right Motors
Building a drone at home is an exciting project. It involves understanding different parts. Motors stand out as crucial components. They determine your drone’s performance. This section dives into selecting the appropriate motors for your DIY drone. Let’s explore motor types, thrust, and power requirements.
Motor Types
Different motors offer various benefits for drones. Your choice depends on your drone’s intended use. Brushed and brushless are the two main types.
- Brushed motors: These are affordable and simple to use. They are suitable for beginners.
- Brushless motors: More efficient and durable. Perfect for advanced drones.
Thrust And Power Requirements
Determining the right thrust and power is vital. They affect your drone’s ability to lift and fly efficiently. Here is a simple guide:
| Drone Weight | Required Thrust |
|---|---|
| Less than 2 kg | 500-1000 grams per motor |
| 2-5 kg | 1000-2000 grams per motor |
Remember, the total thrust should be twice the weight of the drone. Also, consider the battery’s power capacity. Ensure it matches your motors’ requirements for optimal performance.
Propellers And Their Impact
Propellers are the blades that lift a drone off the ground. They are crucial for stable flight. You must choose the right propellers when making a drone at home. The size, material, and design of propellers can affect your drone’s performance. Let’s explore how to select the best propellers for your homemade drone.
Sizing
Proper propeller size ensures maximum efficiency. Size impacts how well a drone can hover and how responsive it is. Use this guide to choose the right size:
- Heavy-duty drones need larger propellers.
- Small drones perform best with shorter propellers.
- The weight of the drone decides the optimal propeller size.
- Check the motor specs for size recommendations.
Material And Design
The right materials and design of the propellers are key for a resilient drone.
| Material | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Plastic | Light and affordable |
| Carbon Fiber | Durable and efficient |
| Wood | Good vibration absorption |
Select a design that complements your drone’s purpose:
- Symmetrical blades provide stability.
- Curved blades can reduce noise.
- Raked tips help improve performance.
The Heart Of The Drone: Flight Controller
The flight controller is the drone’s brain. It commands everything from stability to navigation. Building a drone at home means you need a reliable flight controller. This component gives the drone its edge, allowing it to soar smoothly and respond to your controls.
Capabilities
Flight controllers come with various features. They maintain the balance of the drone and manage navigation. Here’s what a good flight controller does:
- Stabilizes the drone in various conditions
- Processes inputs from remote control
- Supports GPS for better positioning
- Allows autonomous flight modes
- Integrates with sensors for obstacle avoidance
Setup
Setting up your flight controller is a crucial step. These guidelines will help:
- Mount the controller properly on your drone frame.
- Connect the motors and electronic speed controllers (ESCs).
- Install the software and update firmware.
- Configure the settings according to your drone.
- Calibrate sensors within the flight control software.
- Test with short hovering sessions, then proceed to full flight.
Remember to double-check connections and always test in a safe environment.
Powering Your Drone
Welcome to the core of drone-making – Powering Your Drone. Creating a drone at home is thrilling. Ensuring it has the power to soar is essential. This section guides you through the best options for batteries and power management. Get ready to give your homemade drone the energy it needs to take flight!
Battery Options
Drones need a reliable energy source. There are several battery types to consider. Each has its pros and cons. Choose the best fit for your drone’s size and flight time.
- Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries offer high energy storage and are lightweight. They come in various sizes.
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) are heavier but provide steady power.
- Alkaline batteries are easy to find but not suited for longer flights.
Power Management
Managing power extends your drone’s life. A well-planned power system keeps your drone flying smoothly. It prevents crashes due to power loss. Read on for key tips on efficient power management.
- Use a power distribution board (PDB) to manage the flow of electricity.
- Install an Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) for each motor to control speed precisely.
- Monitor battery life with a voltage checker. This tool warns you before power runs out.
Electronic Speed Controllers (escs)
Building your own drone at home is an exciting challenge that rewards you with a unique gadget. Among the critical components you’ll need to understand are the Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs). These tiny pieces of technology are key in managing your drone’s propulsion system.
Functionality
The ESC connects the drone’s motor, battery, and receiver. It regulates the power that motors get from the battery. This control helps the drone fly smoothly. ESCs also protect the motors from electrical damage.
Calibration
Calibration makes sure ESCs work properly with your drone. This process aligns the ESCs to the throttle range of your receiver. Proper calibration ensures your drone responds accurately to your controls.
- Connect each ESC to the motor and flight controller.
- Turn on your transmitter and set throttle to maximum.
- Power up the ESCs to enter calibration mode.
- Listen for beeps confirming calibration mode.
- Lower throttle to complete calibration.
Connecting The Transmitter And Receiver
Welcome to the thrilling world of DIY drones! After assembling the frame and installing the motors, it’s time to dive into the heart of drone operation: connecting the transmitter and receiver. These components are key players in communication. Let’s ensure your drone responds to your every command with seamless precision. Follow these steps to create a bond between the controller and the drone.
Communication Protocols
Choosing the right communication protocol is crucial for your drone’s performance.
- PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) – A common protocol for beginners.
- PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) – Sends multiple signals over one wire.
- SBUS – A newer protocol, fast with great range.
Pairing Process
To establish a connection, follow the pairing process.
- Power on the receiver with the bind plug attached.
- Activate the transmitter’s bind mode.
- Wait for the LED indicator to show a successful link.
- Confirm control by testing directional inputs.
Success in pairing means you’re ready to take to the skies!

Credit: m.youtube.com
Camera And Fpv System Setup
Ready to soar with your homemade drone? An essential piece is the camera and First-Person View (FPV) system. These give you eyes in the sky. Setting them up right is key to a great flight experience. Let’s dive into the exciting world of aerial filming and flying.
Choosing A Camera
Best drone jaunts start with a great camera. Think clarity, stability, and size when picking yours. Cameras range from simple to sophisticated. The right one depends on your use and budget.
- Check resolution—1080p is basic; 4K wows.
- Size matters—lighter cameras mean longer flights.
- Gimbal support gives stable shots.
Fpv Basics
FPV or First-Person View turns you into a pilot’s copilot. It’s like flying without leaving the ground. There are a few things to know.
- FPV system sends live video from drone to you.
- You’ll need a screen or goggles to watch the action.
- Range and quality depend on your gear.
Set up starts with connecting your camera to the transmitter. Then, lace it to receiver and display gear. Testing ensures everything syncs well.
Autopilot And Gps Integration
Mastering autopilot and GPS integration is pivotal for DIY drone enthusiasts. This synergy enhances flight precision, ensuring your homemade drone navigates skies with confidence.
Flying a drone with precision requires more than just manual controls. The integration of autopilot and GPS technologies transforms your homemade drone into a smarter, self-navigating machine. This integration allows your drone to follow pre-set paths, hover in place, and return home automatically. Let’s dive into setting up autopilot systems and GPS modules for your DIY drone.
Types Of Autopilot
- Basic Autopilot: Offers simple functions like altitude hold and returns-to-home.
- Advanced Autopilot: Features multi-waypoints navigation and obstacle avoidance.
- Open-Source Autopilot: Customizable, with a supportive community for enhancements.
Choosing the right type of autopilot depends on your drone’s purpose and desired features. Basic systems suit beginners, while advanced options cater to more complex missions.
Gps Module Setup
Integrating a GPS module with your drone’s autopilot system requires careful setup. Follow these steps for a successful integration:
- Mount the GPS module on the drone’s frame, ensuring a clear view of the sky.
- Connect the module to the autopilot using the appropriate cables.
- Configure the settings via your drone’s software or a dedicated app.
- Test the GPS signal strength and calibrate the compass if necessary.
With the GPS module in place, your drone can accurately pinpoint its location and make reliable navigational decisions. Always perform a test flight in an open area to confirm the system’s reliability before venturing further.
Wiring And Soldering Tips
For DIY drone enthusiasts, solid wiring and soldering form the backbone of a successful build. Delicate connections require precision and care. Let’s dive into making those connections secure and efficient.
Wire Management
Proper wire management ensures your drone remains tidy and functional. It also prevents accidents mid-flight.
- Label wires for easy identification.
- Group wires that connect to the same component.
- Use zip ties to secure loose wires.
- Install heat shrink tubing to protect soldered joints.
- Avoid sharp bends to prevent wire damage.
Soldering Best Practices
Soldering is critical in attaching components securely. Follow these practices for best results.
- Preheat the soldering iron.
- Clean the iron’s tip with a damp sponge.
- Apply a small amount of solder to the iron.
- Heat the wire and pad, not just the solder.
- Let the solder cool naturally. Do not blow on it.
Keep the tip tinned to improve heat transfer. Re-tin as necessary.
Testing Motors And Propellers
Building a drone at home is exciting! After assembling the frame and wiring the electronics, it’s time to test the motors and propellers. This step checks if the drone parts work together well. Testing ensures a safe, successful flight later on.
Bench Testing
Begin with bench testing. This is like a rehearsal before the main event.
- Connect motors to the Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs).
- Secure the drone’s frame to a stable platform.
- Attach a battery to power up the motors.
- Use a software program to control the throttle gradually.
Watch the motors’ reaction to the controls. Listen for consistent buzzing. Ensure each propeller spins the right way. This is crucial for balanced flight later.
Safety Precautions
Handling spinning propellers can be dangerous. Always prioritize safety.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes.
- Keep hands and loose clothing away from moving parts.
- Ensure no pets or small children are near the testing area.
- Start tests at the lowest power setting before gradually increasing.
- Check that the propellers are firmly attached, but do not over-tighten.
Double-check all connections before powering up. A loose wire can cause a short circuit. Test in a well-ventilated space. This prevents overheating of components.
Firmware And Software Configurations
Building a drone at home is thrilling. Once you assemble the hardware, breathe life into it with the right firmware and software. This section guides you through setting up the brain of your drone. Computers use software. Drones use firmware. Updated firmware makes drones smarter and safer.
Firmware Installation
Firmware installation is the key step in drone making. This is like adding a mind to your drone’s body.
- Choose the right firmware for your drone’s flight controller.
- Connect the flight controller to your computer.
- Use a dedicated software tool to flash the firmware onto the flight controller.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure proper installation.
Your drone’s hardware and firmware must match. Check compatibility before starting.
Fine-tuning Settings
Once the firmware is installed, fine-tuning is crucial. This ensures a smooth flight experience.
- Access the drone’s configuration software on your computer.
- Calibrate the sensors for accurate flight data.
- Adjust the PID settings to control how the drone flies.
- Test the settings in a safe environment.
A well-tuned drone responds quickly and predictably. Take the time to get it right.
First Flight And Calibration
Embarking on your first drone flight is an exhilarating experience. Proper calibration sets the foundation for stable, controlled maneuvers. Follow these steps to ensure a successful maiden voyage for your home-built drone.
Pre-flight Checks
Verify your drone’s readiness before takeoff to avoid mishaps. Perform these pre-flight checks:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely in place.
- Check for firm propeller attachments.
- Confirm the remote control is functioning.
Trimming And Adjustments
Proper trimming ensures your drone flies straight and level. Follow these steps:
- Place the drone on a flat surface.
- Initiate the calibration sequence as per the manual.
- Adjust the trim settings if the drone drifts.
Repeat adjustments until the drone hovers without drifting.
After these steps, your drone is set for its first flight. Enjoy the thrill of piloting your creation with confidence!
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Building your own drone can be thrilling yet tricky. Sometimes, things go south. When they do, pinpointing the problem is key to soaring success. Let’s solve common issues that can keep your drone grounded.
Vibration Problems
Shaky flights beg for attention. Follow these steps to smooth things out:
- Check Propellers: Ensure they’re not damaged.
- Balancing Act: Balance each propeller on a balancer.
- Motor Mounts: Tighten loose mounts.
- Firmware: Update to the latest software.
- Rubber Dampers: Use them to reduce vibrations.
Connectivity Challenges
Dropped signals can be a pilot’s nightmare. Combat connectivity woes with these tips:
- Update: Make sure all firmware is current.
- Antenna Position: Adjust for optimal signal.
- Obstructions: Fly in open areas away from interference.
- Range Check: Test control distance.
- Battery Check: Confirm batteries are charged.
Maintenance And Upgrades
Maintaining and upgrading your homemade drone ensures long-term enjoyment and top-notch performance. Understanding the basics of regular check-ups and component enhancements is crucial. A well-maintained drone provides smoother flights and fewer crashes. Upgrading parts can unlock new potential. This guide outlines essential steps for keeping your drone in prime condition.
Regular Maintenance
Regular checks keep drones flying safely. Follow these simple steps:
- Inspect the propellers for damage.
- Check all screws and tighten them.
- Clean the camera lens for clear footage.
- Look for loose connections in the wiring.
- Test battery life and replace if needed.
Record findings in a maintenance log. This helps track drone health.
Upgrading Components
Upgrading components boosts drone capabilities. Consider these popular upgrades:
- Install high-capacity batteries for longer flights.
- Add powerful motors to increase speed and lift.
- Upgrade the camera for higher quality images.
- Enhance the navigation system for better control.
| Component | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Battery | Extended Flight Time |
| Motor | Improved Speed |
| Camera | Sharper Images |
| GPS Module | Accurate Positioning |
Select components compatible with your drone model. Check the user manual before buying upgrades.
Community And Resources
Building a drone at home is a fun challenge. To start this project, you need the right information. You can find help through communities and resources online. Let’s dive into where you can find tips and tricks to build your homemade drone.
Online Forums
Forums are great places to meet people who love drones. People in these forums share ideas. You can ask questions and get answers from experts. Some popular forums are:
- DIYDrones: A place for all skill levels to discuss building drones.
- RCGroups: Here, find threads about remote control aircraft, including drones.
- Multirotor Forums: Focuses on multirotor drones and has many build logs.
Remember to read the rules of each forum. Be polite and say thank you when you get help!
Further Learning
You want to know more about drones. The internet has many courses for this. You can watch videos or take online classes. Some resources are:
- YouTube Channels: Watch tutorials about building and flying drones.
- Online Courses: Websites like Udemy offer full courses on drone technology.
- eBooks and Guides: Read in-depth guides on every aspect of drone-making.
Choose resources that match your learning style. Spend time practicing. Soon, you could fly a drone you made at home!

Credit: www.instructables.com
Conclusion
Building your own drone can be an exhilarating challenge. With the right tools and guidance, you’ve learned that it’s completely achievable. Whether for a hobby or educational purposes, the skills you gain are invaluable. Remember to stay patient, follow safety guidelines, and let creativity soar as high as your new homemade drone!